
Hearing Loss Regenerated in Damaged Mammal Ear The Personal Longevity
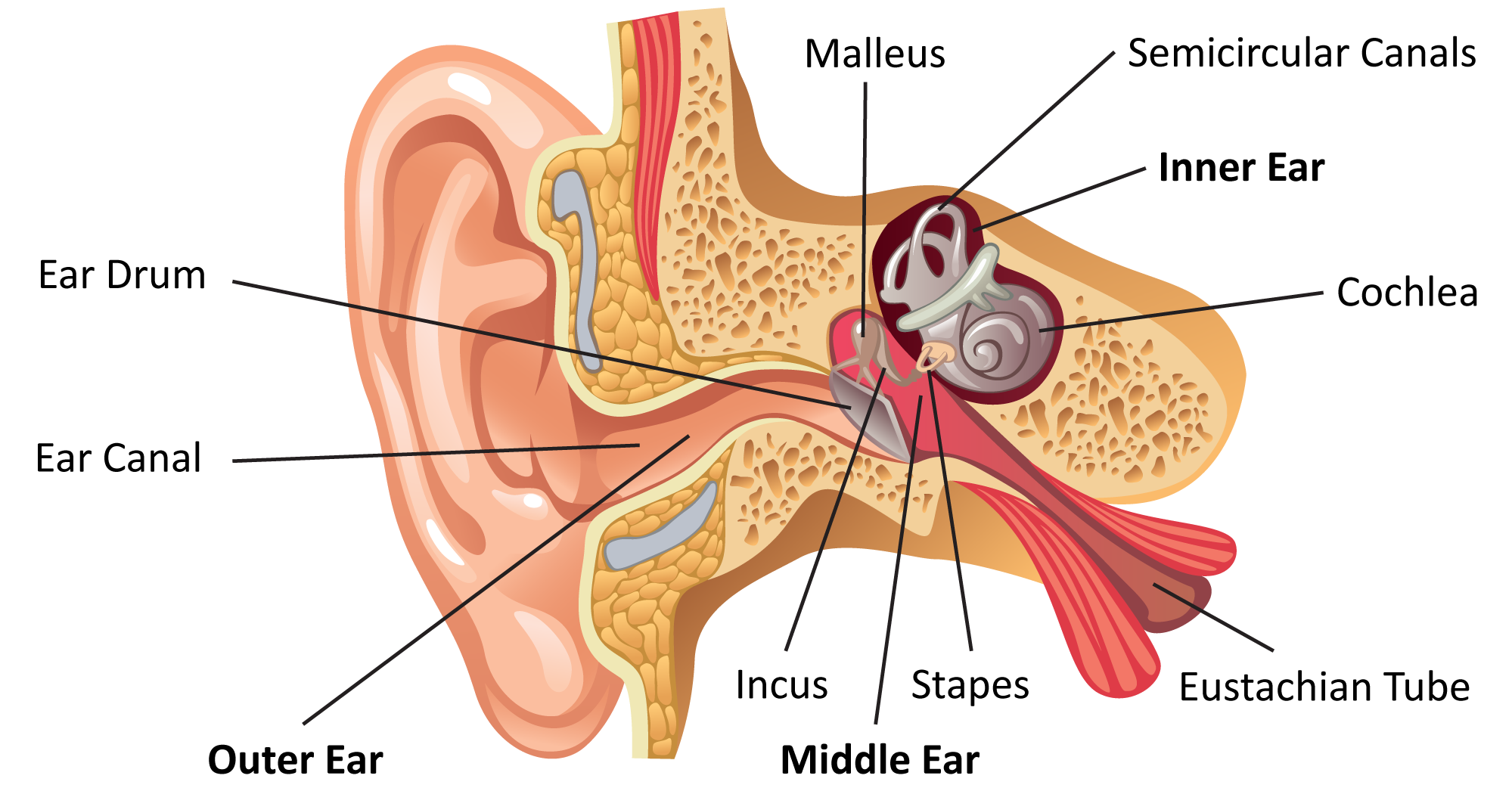
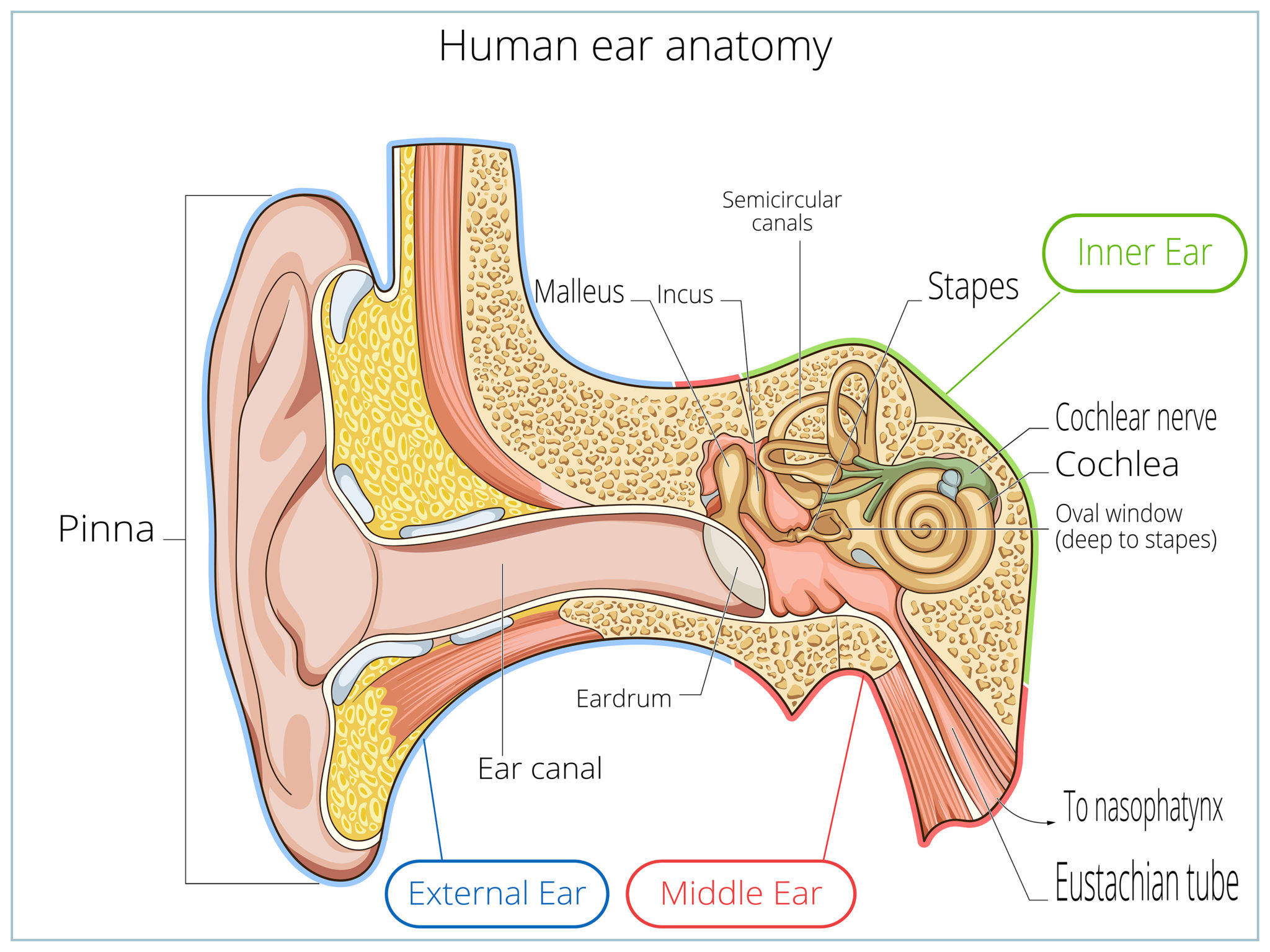
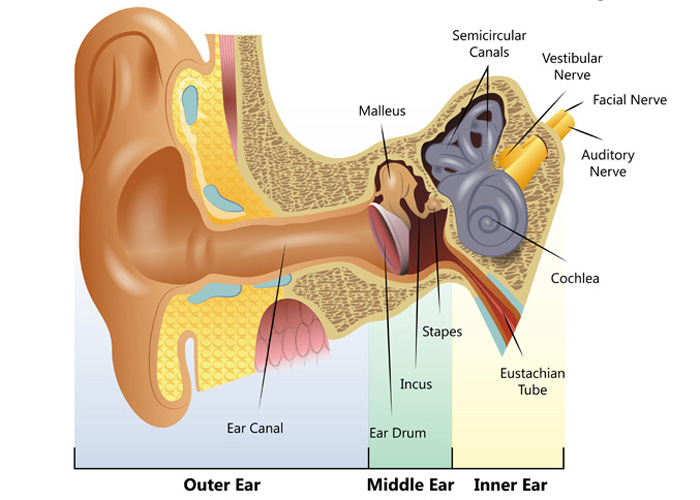
The inner ear is the innermost part of the ear and consists of the cochlea, auditory nerve, vestibule and semicircular canals. The inner ear is a maze of tubes and passages, referred to as the labyrinth. The inner ear is mainly responsible for balance and detecting sound. The cochlea contains the cells responsible for hearing, the auditory.
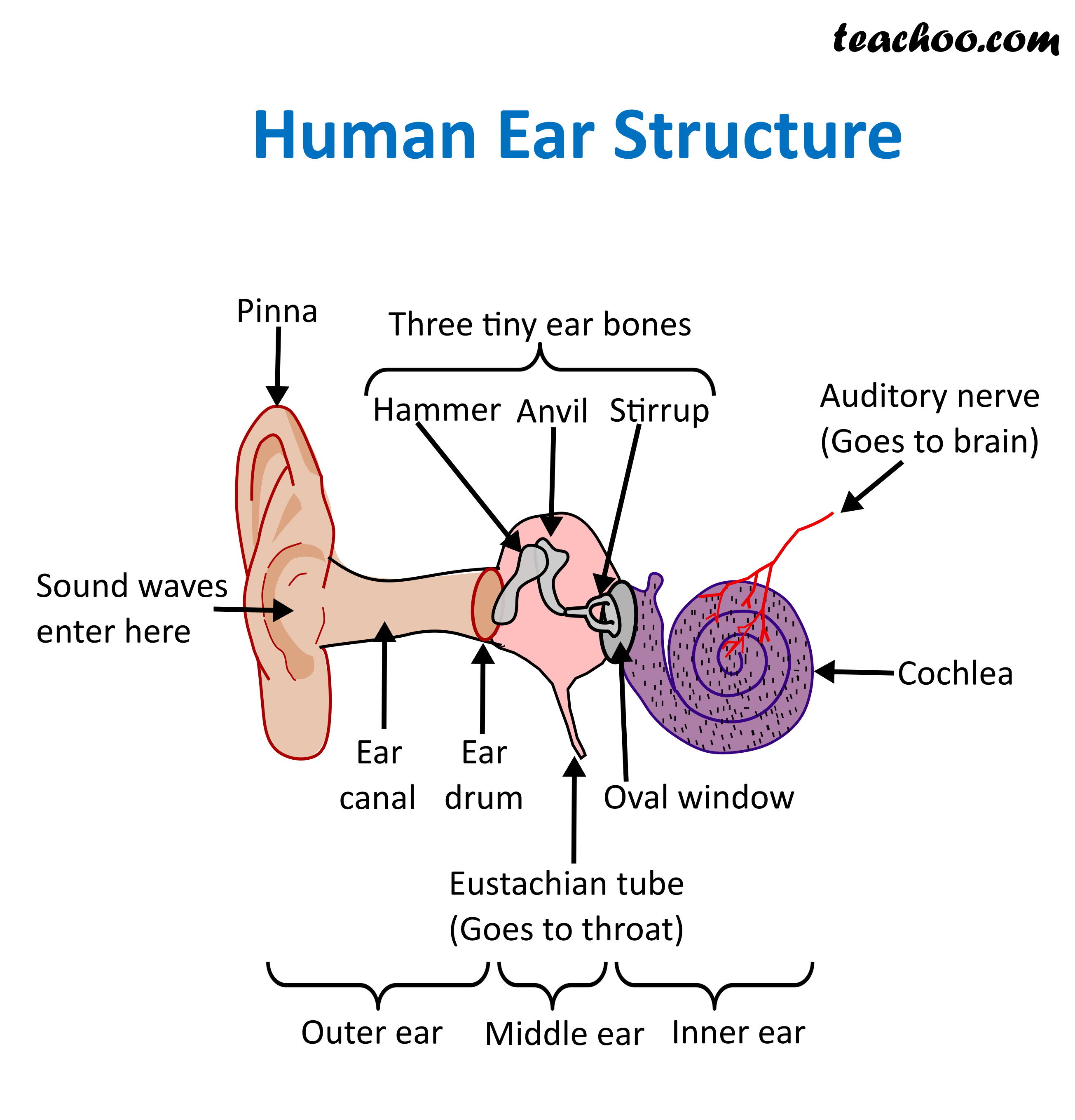
Structure and Function of Human Ear with Diagram Teachoo
Ear cartilage structures are part of the outer ear, which is also called the external ear in medical and anatomy textbooks. The following ear diagram depicts the inner ear, which contains sensory.

Inner Ear Problems Causes & Treatment of inner ear Dizziness & Vertigo
A bony casing houses a complex system of membranous cells. The inner ear is called the labyrinth because of its complex shape. There are two main sections within the inner ear: the bony labyrinth.
How We Perceive Sound
The external ear is the visible part of the hearing apparatus. It is comprised of the auricle (pinna) and external auditory canal, including the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. Together with the tympanic membrane and the middle ear, the pinna serves to amplify sound. The pinna acts as a funnel to deliver sound to the external acoustic meatus, and the external auditory canal.
Audition and Somatosensation Anatomy and Physiology I
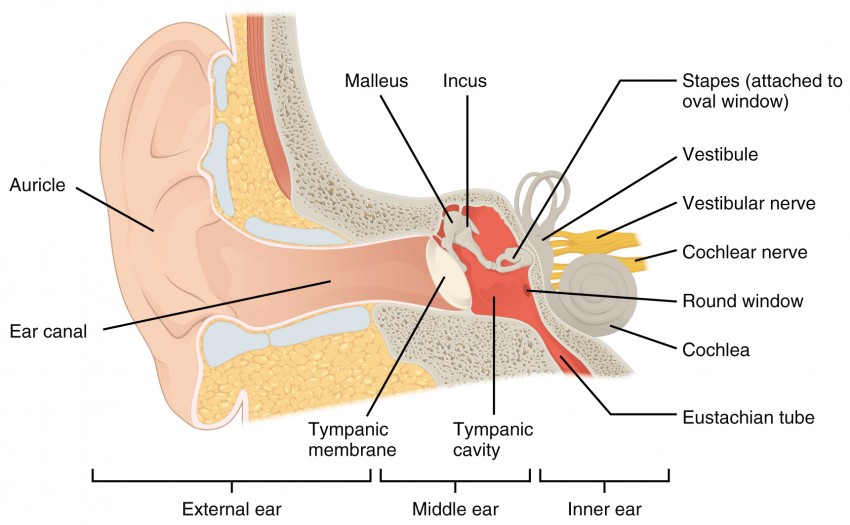
Ear Anatomy - Inner Ear. Ear Anatomy Schematics. Ear Anatomy Images. Chapter 4 - Fluid in the ear. Fluid in the ear Discussion. Fluid in the ear Outline. Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes. Fluid in the ear Images. Chapter 5 - Traveler's Ear.
Outer ear diagram
That's why labeling the ear is an effective way to begin your revision. It helps you to memorize the names and their locations, which in turn will aid you to remember their functions. Below, you can download both the blank ear diagram to make some notes, and then try labeling the ear using the unlabeled ear diagram. Good luck!
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
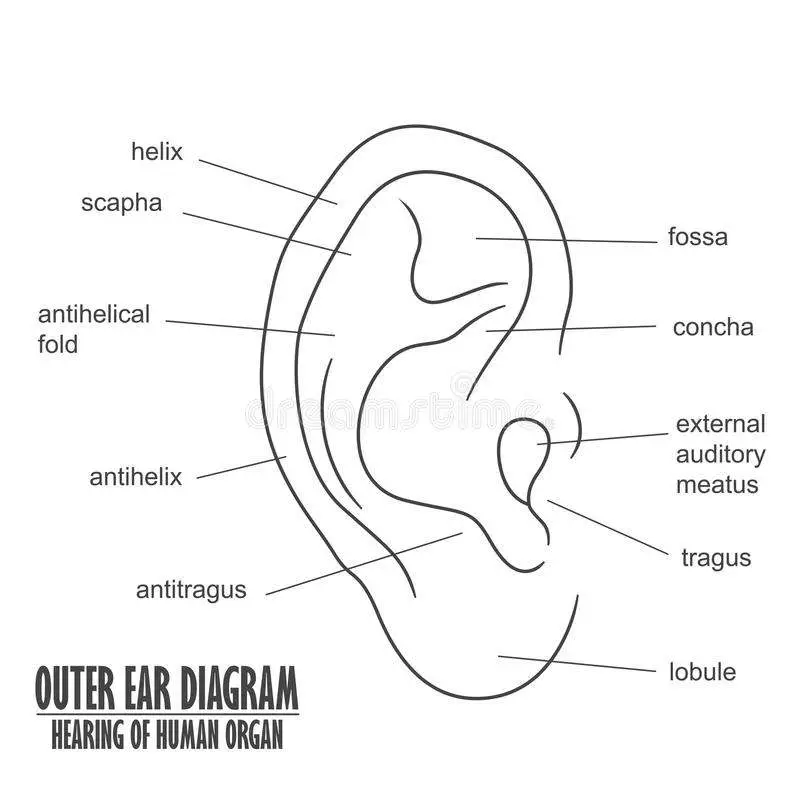
Helix: The outermost curvature of the ear, extending from where the ear joins the head at the top to where it meets the lobule. The helix begins the funneling of sound waves into the ear; Fossa, superior crus, inferior crus, and antihelix: These sections make up the middle ridges and depressions of the outer ear. The superior crus is the first ridge that emerges moving in from the helix.

Disorders of the Ear Part Two a PA Review and Podcast
Figure 1.Anatomy of the external ear. 4 Innervation of the auricle. The auricle has several sources of sensory innervation:. The superficial surface is supplied by the great auricular nerve and lesser occipital nerve, both of which are branches of the cervical plexus (C2 & C3), and the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve, which is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V)
HEARING ANATOMY AND PROCESS AUDIOLOGIS
The diagram of the ear is important from Class 10 and 12 perspectives and is usually asked in the examinations. A brief description of the human ear along with a well-labelled diagram is given below for reference. Well-Labelled Diagram of Ear. The External ear or the outer ear consists of; Pinna/auricle is the outermost section of the ear.

Alila Medical Media Human ear anatomy, labeled diagram. Medical
The Structure of Human Ear. Helix: It is the prominent outer rim of the external ear. Antihelix: It is the cartilage curve that is situated parallel to the helix. Crus of the Helix: It is the landmark of the outer ear, situated right above the pointy protrusion known as the tragus. Auditory Ossicles: The three small bones in the middle ear.
The Ear CP Blas de Otero
The ear canal connects the outer cartilage of the ear to the eardrum, which allows people to hear. Read on to learn more about the ear canal.. Anatomy, head and neck, ear. https://www.ncbi.nlm.

How The Ear Works
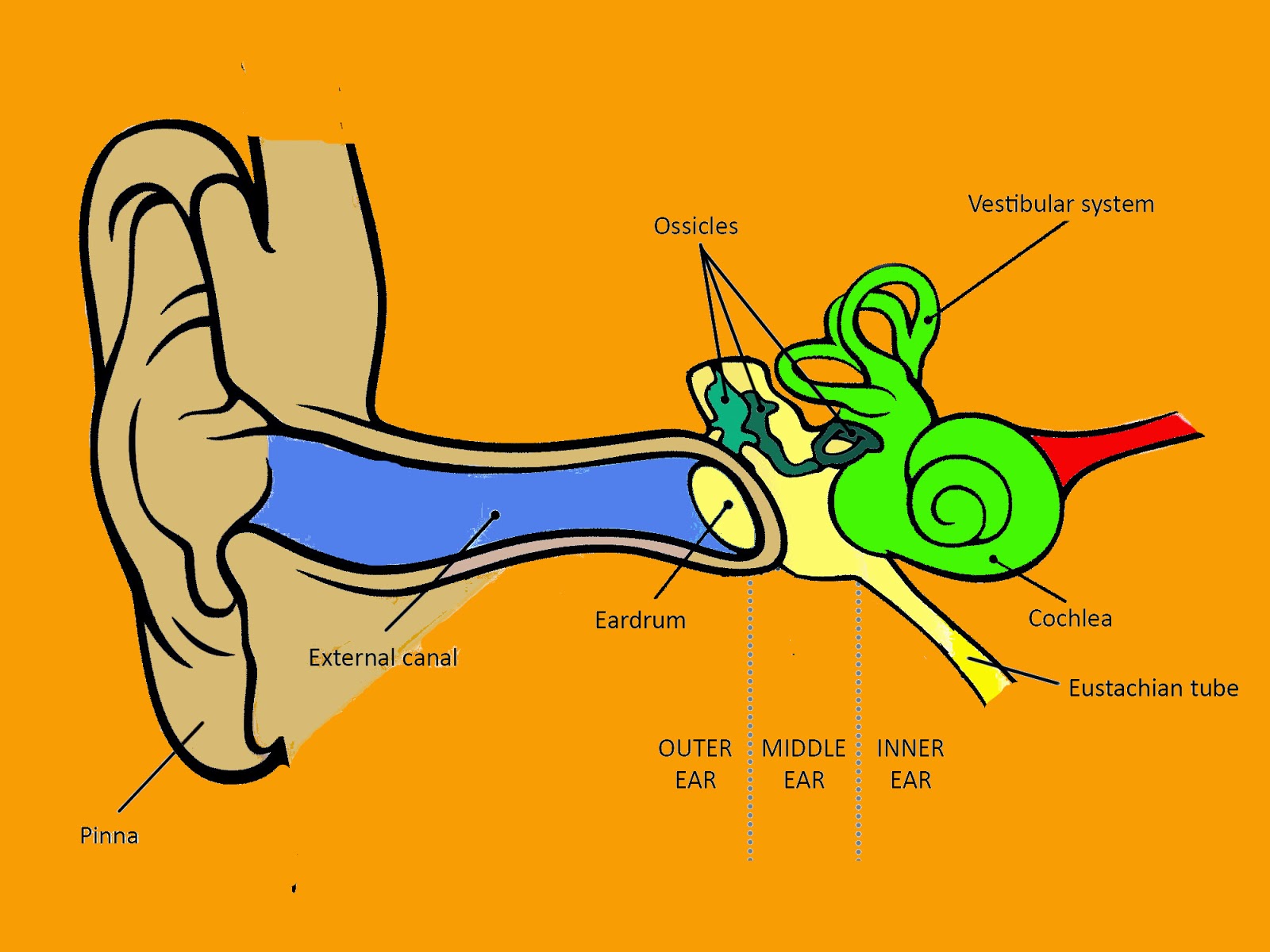
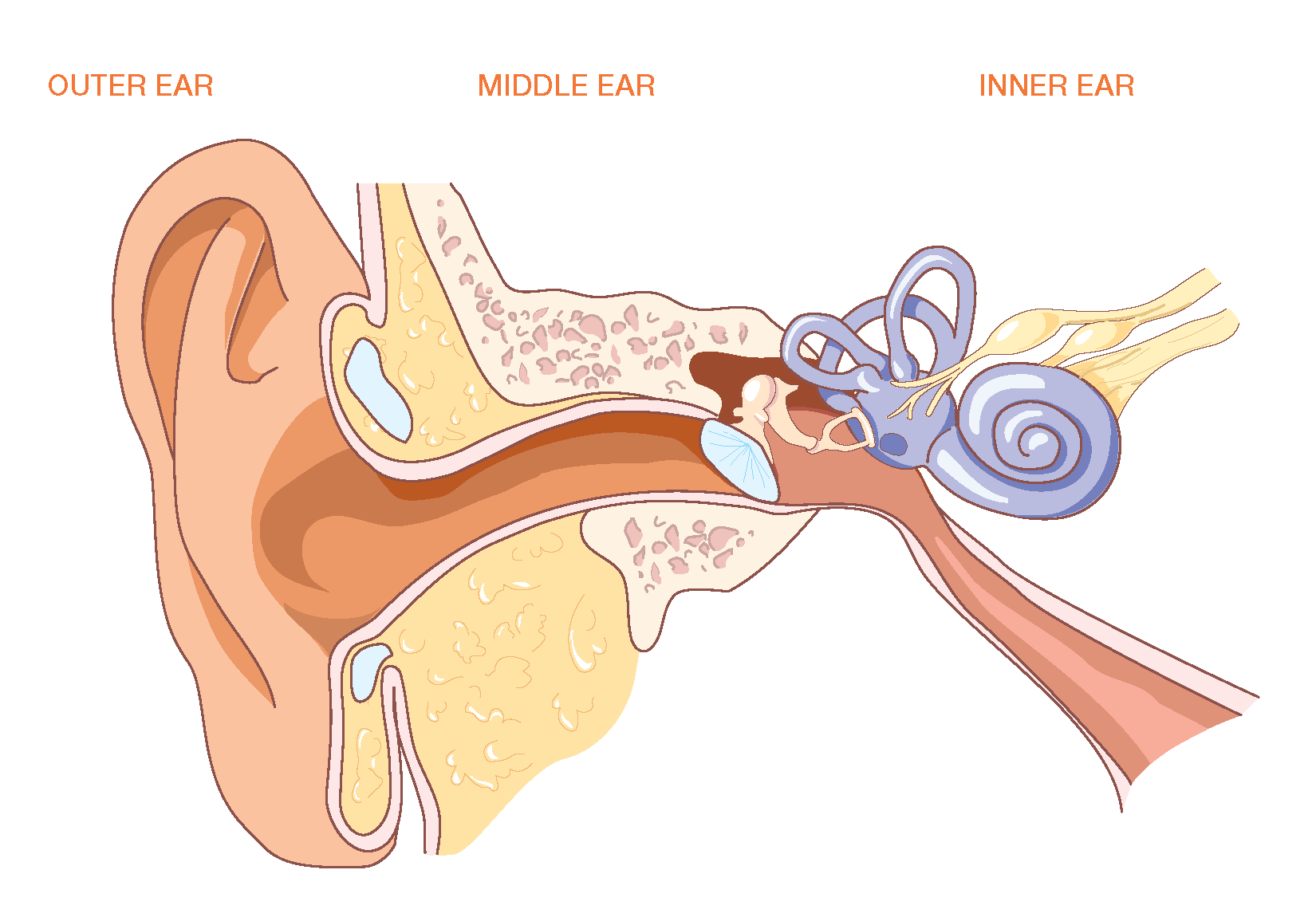
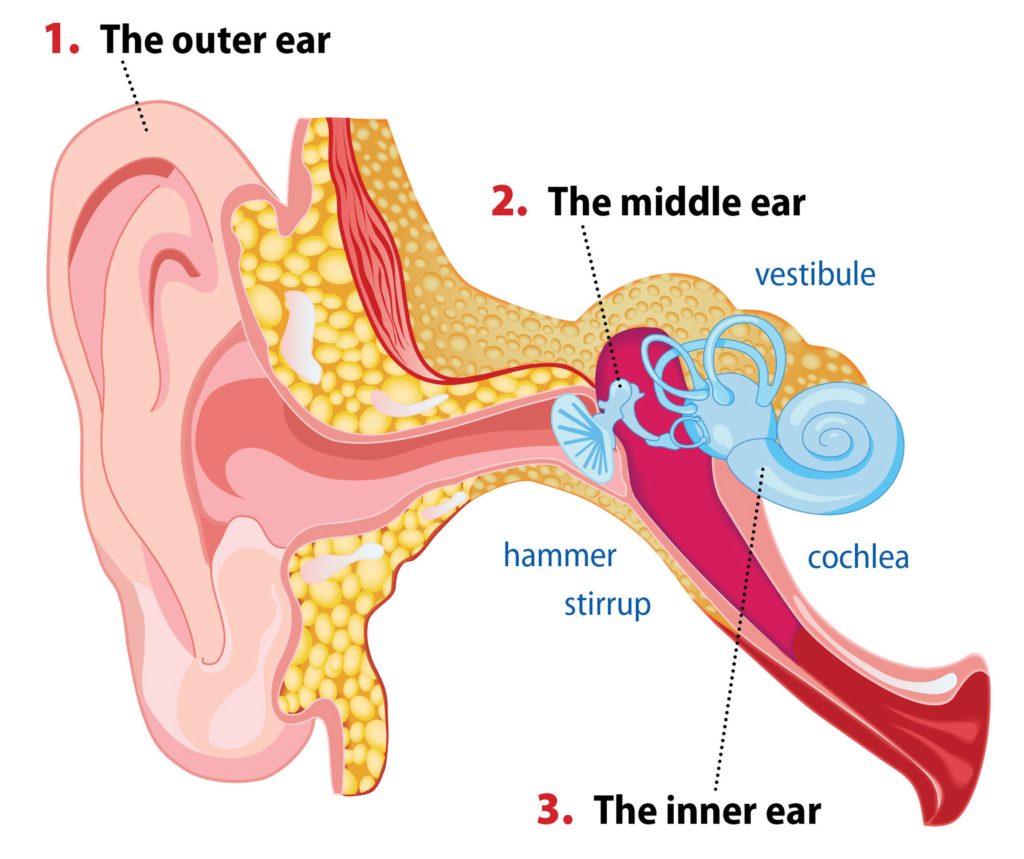
The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. It is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. The main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance. The ear is anatomically divided into three portions: External ear. Middle ear.

Vertigo Have You Spinning Chiropractic Home Care Ear anatomy, Human
Your inner ear is the last stop that sound waves make in a carefully orchestrated journey that starts from your outer ear. These waves travel from your outer ear through your middle ear to your inner ear. In the inner ear, the sound waves are converted into electrical energy, which your hearing nerve delivers to your brain as sound, making it.

Ear Diagram Leaving Cert Human Anatomy
The ear diagram is one of the important topics for Class 10 and 12 students of the CBSE board and in this article, we will briefly explain the structure of the ear, its different parts and their functions. Parts of the Human Ear. The human ear consists of three different parts. These are: The outer ear. The middle ear. The inner ear
Common balance disorders Hearing Link
Your inner ear contains two main parts: the cochlea and the semicircular canals. Your cochlea is the hearing organ. This snail-shaped structure contains two fluid-filled chambers lined with tiny hairs. When sound enters, the fluid inside of your cochlea causes the tiny hairs to vibrate, sending electrical impulses to your brain.
What is conductive hearing loss? Blog of Kiversal
The human ear, like that of other mammals, contains sense organs that serve two quite different functions: that of hearing and that of postural equilibrium and coordination of head and eye movements. Anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear.The outer ear consists of the visible portion called the auricle, or pinna, which projects from the side of.